The Better Regulation Delivery Office analyzed 355 acts regulating business activities in Ukraine by using the Rolling Review method in the first quarter of 2016. The BRDO identified three trends based on the results of the analysis performed:
- every fourth act bears marks of being illegal;
- every third act was not brought in compliance with the current legislation;
- none of analyzed acts has supporting documents on the regulatory impact analysis and monitoring the appropriate effects that makes it impossible to determine the impact of acts with these documents.
The BRDO activity with regard to establishing a new type of the business regulation system is conducted simultaneously in several areas:
- the Rolling Review of the existing regulation;
- new regulation firewall; and
- drafting regulatory acts.
One the main problems of small and medium-sized businesses in Ukraine is a low quality regulatory environment. Business in Ukraine can never be sure that all the legal requirements for doing business have been met. This due to the fact that:
- soviet acts are still valid in Ukraine;
- the number of valid regulatory acts is constantly increasing (according to the BRDO review, the number of basic laws, resolutions and instructions is annually increased by more than 1200 acts);
- existing acts often contradict each other and create business rules that can be fulfilled.
To deal with these problems, the BRDO developed a standardized process of systematic review of regulatory acts by using the Rolling Review method that provides for a comprehensive assessment of the current regulatory legislation on such criteria as legality, necessity, corruption risks, business convenience and others.
The review will be resulted in a decision taken on each act: to recommend to abolish, revise or save. The BRDO sends the packages of draft regulations providing for the abolition or making amendments to regulators to establish an effective regulatory environment.
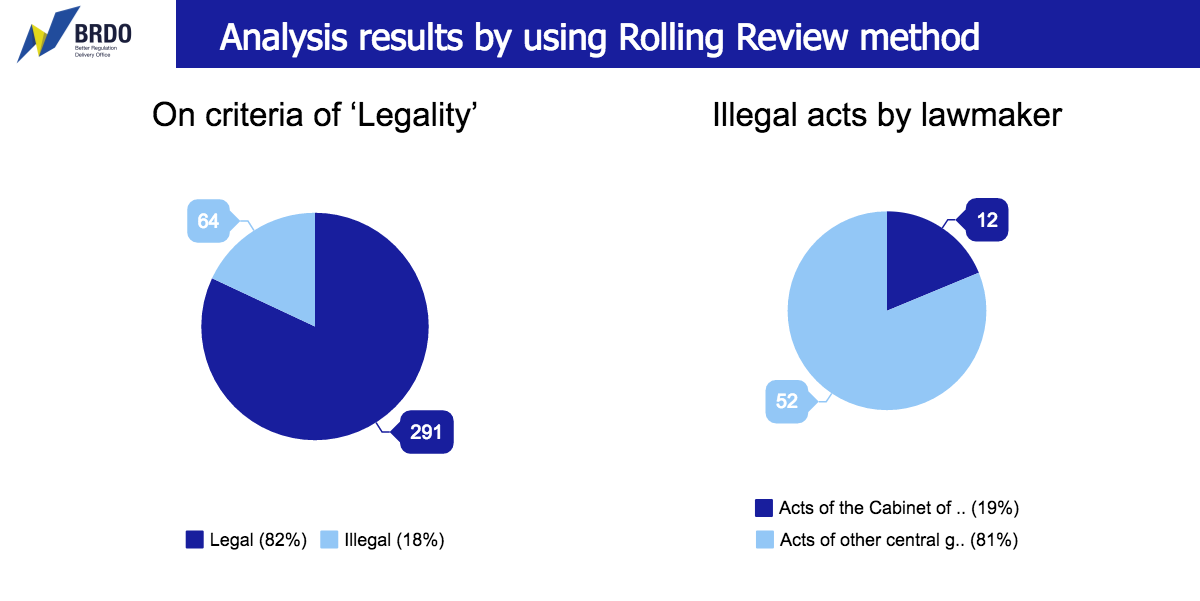
Legality. 12 acts of the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine and 52 acts of ministries and other central government bodies bear marks of being the ones that don’t meet the basic criteria of legality. The review of legality includes verifying reasonable grounds to adopt a subordinate regulation and the registration in the Ministry of Justice of Ukraine.
The structure of the Ukrainian legal system provides for a direct hierarchy of regulations: subordinate regulations should be adopted on a ground, within the powers and in a way envisaged by the Constitution and laws of Ukraine. In cases when subordinate regulations are adopted in violation of this principle, the rules become unpredictable for business and the legal protection is complicated. Resources spent by business to deal with these problems are the money that the Ukrainian economy loses as high transaction costs.
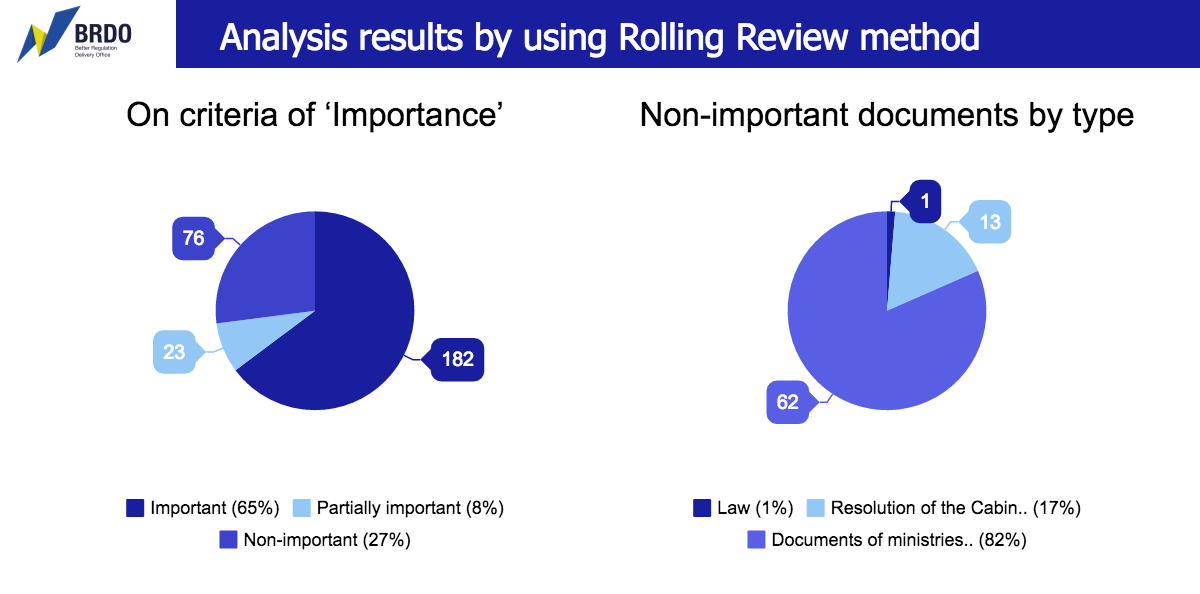
Importance. Based on the results of the BRDO review, 76 acts have been identified as being non-important, 23 – as being partially important and 182 – as important. This means that a large number of existing regulations were not brought in compliance with the current legislation and are likely to contain contradictory rules for business.
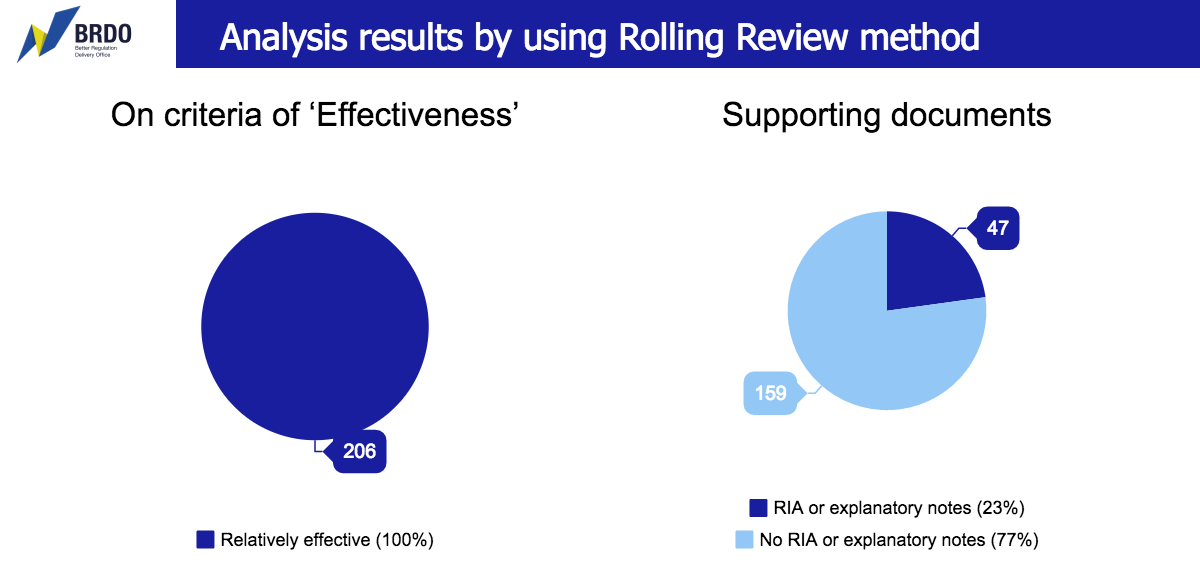
Effectiveness. Based on the results of the BRDO review, 206 regulatory acts have been identified as being relatively effective – that is, their effects can’t be determined by using supporting documents on the regulatory impact analysis.
The adoption of a regulatory act provides for achieving a certain purpose clarified in supporting documents – explanatory notes or the regulatory impact analysis (RIA). It is possible to find out whether the effectiveness of this act can be determined by using these documents only on the basis of their availability or non-availability and the clearly measurable criteria included. Thus, only 47 documents had explanatory notes or the RIA while only 3 of them contained measurable indicators of effectiveness. None of the analyzed acts has documents on monitoring appropriate effects, by using of which the effectiveness of the act could be determined. In a case, when there is no analysis of the state policy effectiveness conducted, the state and the society are deprived of key indicators of effectiveness, without which it is impossible to work on improving the regulation.
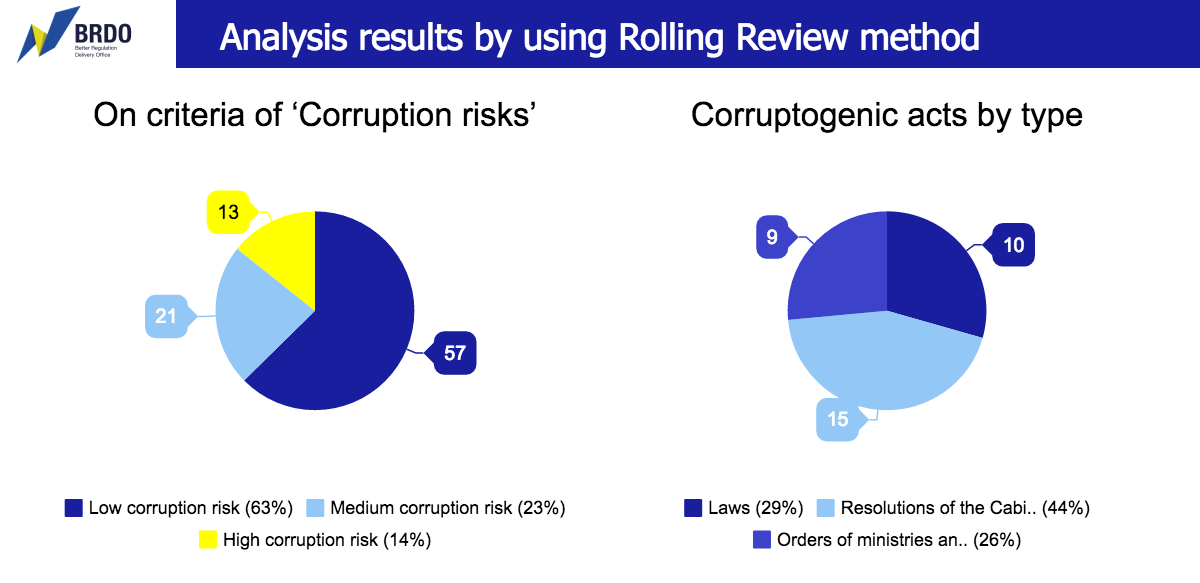
Corruption risks. The review for corruption risks found out that 34 regulatory acts had a medium and high level of corruption. This includes 10 laws, 15 resolutions of the Cabinet of Ministers and 9 orders of ministries and other central government bodies.
This method provides that a regulatory act should be assessed on the basis of a number of points, including: a number of contacts of an official and an entrepreneur available, a need for officials to take decisions on granting permits or prohibiting activities, the availability of clear criteria to take decisions and appeals deadlines.
Convenience for business. Based on the assessment of regulatory acts impact on business processes, 12 regulatory acts having a high or medium risk for the freedom of doing business have been identified. There are 5 laws of Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, 5 resolutions of the Cabinet of Ministers and 3 orders of ministries and other central government bodies among them.
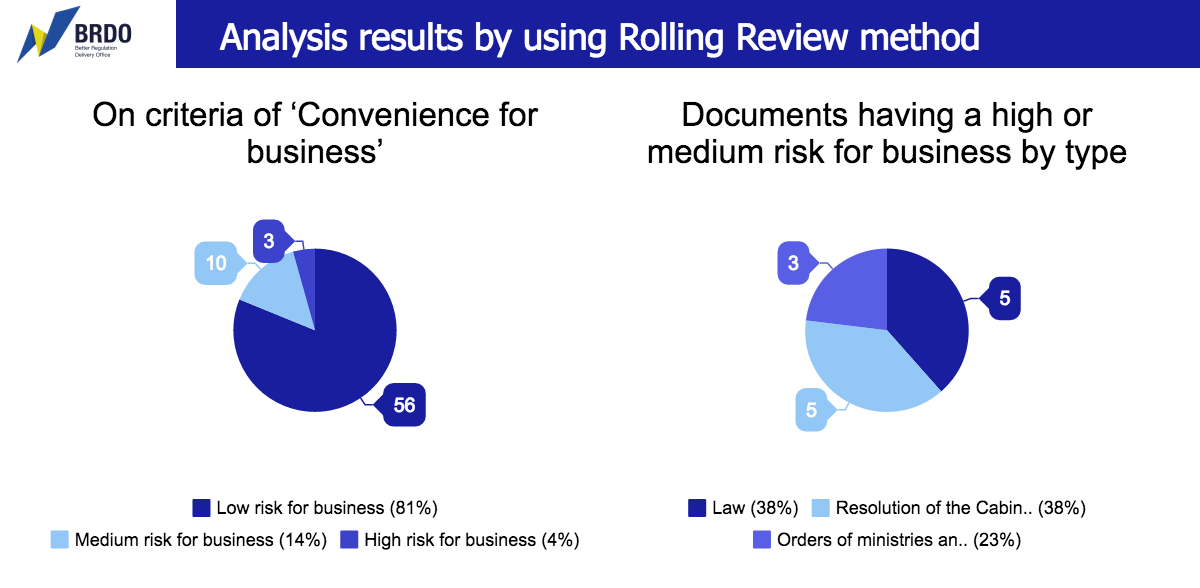
Totally, 355 regulatory acts were reviewed on criteria of legality, 281 – on criteria of importance, 206 – on criteria of effectiveness, 90 – on criteria of corruption risks, 69 – on criteria of impact on business.
Detailed review can be found on the BRDO website.